
Core solution
Compound Feed Manufacturing
Compound Feed Manufacturing (CFM) is a global standard for the production processes of aquaculture and livestock feed mills. It covers all stages of production, from the purchase and handling of raw materials to the processing and distribution of finished feed.
Transparency and traceability on farm inputs
What is Compound Feed Manufacturing?
Compound Feed Manufacturing (CFM) aims to provide manufacturers with clarity on market requirements and act as a practical manual for feed mill operations. Created in collaboration with stakeholders from across the sector, it helps to promote suitable animal nutrition, safeguard feed and food safety, and set strict requirements on the origins and responsible sourcing of raw materials used to manufacture feed. CFM is a mandatory sourcing requirement for compound feed destined for aquatic species covered by the Integrated Farm Assurance (IFA) for aquaculture standard, enhancing traceability at all stages of the production chain. CFM-certified production processes account for more than 20 million metric tons of compound feed in the market every year.
CFM at a glance
A global standard
for any operation that is legally responsible for compound feed manufacturing
Covers all stages
of production, from the purchase and handling of materials to the distribution of finished feed
Required for mills
supplying aquaculture farms with IFA-certified production processes
Provides voluntary options
for additional product attributes on environmental and social governance
Specifies fixed percentages
of ingredients that must be sourced from responsible production, such as soy, fish meal/oil, and palm oil
Requires the individual audit
and certification of each manufacturing site for multisite feed mill operators
A global standard
for any operation that is legally responsible for compound feed manufacturing
Provides voluntary options
for additional product attributes on environmental and social governance
Covers all stages
of production, from the purchase and handling of materials to the distribution of finished feed
Specifies fixed percentages
of ingredients that must be sourced from responsible production, such as soy, fish meal/oil, and palm oil
Required for mills
supplying aquaculture farms with IFA-certified production processes
Requires the individual audit
and certification of each manufacturing site for multisite feed mill operators
Which topics does CFM address?
CFM was developed together with sector experts and through consultation with a range of feed mill operators, ingredient suppliers, and producers from around the world. Our approach to standard setting ensures that CFM remains robust, realistic, and cost-efficient for manufacturers while meeting the evolving demands of buyers.
Core topics in CFM v3.1 include:
Feed safety
Traceability
Responsible sourcing
Raw material management
Prohibited materials
Workers’ competence
Workers’ health, safety, and welfare
Site hygiene and management
Resource use
Biosecurity
Discover more about how CFM helps you address feed sector challenges.

Who should use CFM?
Any operation or company that is legally responsible for the manufacturing of compound feed can gain CFM certification. Manufacturers can get certified in any country where a GLOBALG.A.P. approved certification body (CB) conducts audits.
Grazing and foraging materials, and home-mixed feed which does not leave the farm where it has been produced, are not covered by CFM. Aquaculture producers who prepare home-mixed feed must follow the requirements outlined in IFA for aquaculture.
Manufacturers seeking to supply their products to aquaculture producers with IFA-certified production processes must have certification to CFM or a recognized feed safety scheme. This is a mandatory requirement for aquaculture producers with IFA certification.
How does CFM work?
Compliance with the standard requirements is audited annually by an accredited and independent third-party CB.
Manufacturers can choose from any GLOBALG.A.P. approved CB active in the relevant country.
A successful CB audit results in a certificate valid for one year.
CFM certification is required for each individual manufacturing site (Option 1). For multisite feed mill operators, all sites must be audited separately.
The standard is composed of control points and compliance criteria (CPCCs). CPCCs are graded in three levels: Major Must, Minor Must, and Recommendation.
Control points
Fundamentals that set the foundation of a GLOBALG.A.P. requirement
Written in question form
Compliance criteria
Methods that producers can use to demonstrate compliance
Evidence required for demonstrating that the outcome is achieved
Read more about the audit process and standard requirements.

How is certification status verified?
Every producer registered in the GLOBALG.A.P. certification system is assigned a 13-digit GLOBALG.A.P. identification number (e.g., a GLOBALG.A.P. Number (GGN)). This number allows verification of certification status in the GLOBALG.A.P. IT platform, upholding our rigorous transparency requirements throughout the supply chain.
For aquaculture producers with IFA certification, the GGNs of their feed suppliers are also displayed in the GLOBALG.A.P. IT platform.
Manufacturers can control data access and privacy rights for audit reports, and the reports are not shared publicly or with third parties. This process is handled via your chosen CB.
What are recognized feed safety schemes?
Manufacturers that seek to sell their feed to aquaculture producers with IFA-certified production processes must be certified to either CFM, a standard successfully benchmarked against CFM, or a feed scheme accredited to ISO/IEC 17065 or 17021.
Based on ISO/IEC accreditation, certification to the following third-party feed safety schemes is accepted as compliant with the sourcing requirements in IFA for aquaculture. However, these schemes are not considered officially equivalent or benchmarked to CFM.
FSSC Feed (including PAS 222)
SQF Code for Feed
Universal Feed Assurance Scheme (UFAS)
In addition to certification against one of the above-mentioned feed safety schemes, feed manufacturers must be audited by a GLOBALG.A.P. approved CB for the CFM standard against the requirements in CFM v3.1 section A5, section B, and section C.

Corporate news and events have moved!
All the latest updates can now be found on the Agraya website – connecting people, ideas, and solutions across the global farming network.
Looking for technical news?
Technical news updates for core solutions can be found in our technical news libraries.
Demonstrate your commitment to responsible production practices
Why choose Compound Feed Manufacturing?
Compound Feed Manufacturing (CFM) seeks to enable manufacturers to assess, demonstrate, and improve safe and responsible production practices. Requested by buyers across the globe, the standard provides a practical path for manufacturers to implement feed mill best practices that help contribute to the long-term viability of the sector, the safeguarding of animal health, and the protection of workers’ safety and welfare.
Which industry challenges does CFM address?
Safe, suitable nutrition is vital for animal health and welfare. Manufacturing standards play a key role in feed and food safety across the supply chain.
In addition, the origins and responsible sourcing of raw materials used to manufacture feed are increasingly important to consumers, particularly with regard to land conversion.
Environmental criteria are therefore required to promote both responsible resource use in production and the responsible sourcing of critical compounds such as soy, fish meal/oil, and palm oil.
Responsible production is also about people, and workers’ health, safety, and welfare are in the spotlight due to new legislation in global supply chains.
Traceability at every stage of the manufacturing process and transparency on the feed used on aquaculture/livestock farms is now a major priority for value chain stakeholders.
Follow our five steps to certification to get started today.
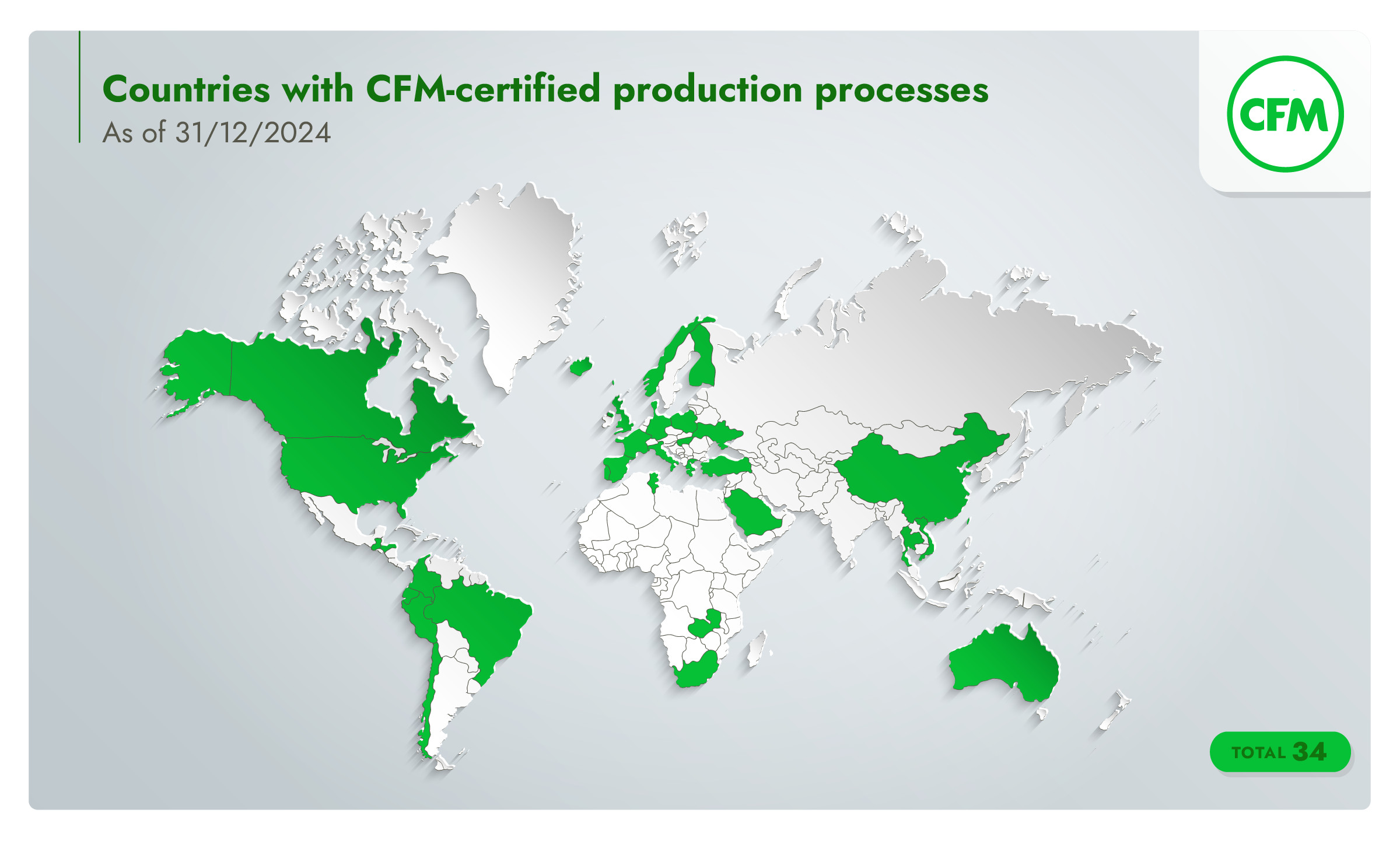
CFM in numbers (as of 31/12/2024)
172
manufacturers under certification
34
countries with certified production processes
21.2 million
metric tons from certified production
172
manufacturers under certification
34
countries with certified production processes
21.2 million
metric tons from certified production

What are the benefits for manufacturers?
Optimize production processes and feed mill management, from workers’ welfare to quality control.
Mitigate feed safety and reputational risks throughout the manufacturing process.
Demonstrate commitment to transparency, social responsibility, and animal health and welfare.
Promote the responsible sourcing of raw materials and critical compounds used to manufacture feed such as soy, fish meal/oil, and palm oil.
Fulfill the requirements of international supply chains and gain recognition for safer and more responsible production practices.
Connect with producers with internationally recognized Integrated Farm Assurance (IFA) certification for aquaculture.
Choose from an extensive worldwide network of accredited, GLOBALG.A.P. approved certification bodies (CBs).

What are the benefits for supply chain stakeholders?
Promote traceability and mitigate feed safety and reputational risks throughout the manufacturing process.
Demonstrate commitment to supply chain transparency, social responsibility, and animal health and welfare.
Avoid marine ingredients from Illegal, Unreported, and/or Unregulated (IUU) fishing, including endangered species listed on the IUCN Red List and in the CITES convention.
Benefit from strict sourcing requirements for plant-based ingredients, such as those from areas of illegal deforestation or high conservation value, in line with the FEFAC guidelines for soy.
Support industry-driven smart farm assurance solutions – developed by the sector, for the sector.
Allow potential buyers to easily identify you as one of the growing global pool of certified suppliers that fulfill their requirements.
Benefit from certification verification through the GLOBALG.A.P. IT platform.

Maintaining trust in GLOBALG.A.P. certification
The GLOBALG.A.P. Integrity Program was founded in 2008 as the first of its kind in food certification. Designed to ensure the consistent delivery and implementation of GLOBALG.A.P. standards and add-ons worldwide, the program monitors and assesses all aspects of the third-party certification process.
Which solutions can be combined with CFM?
We offer a range of standards and add-ons targeted to specific aspects of production and the supply chain. They can each be audited or assessed in combination with CFM, extending the certification scope and offering buyers specific assurance tailored to their preferences.
Learn more about GLOBALG.A.P. smart farm assurance solutions.
You may also be interested in...
NON-GM/“Ohne Gentechnik” Add-on
The NON-GM/“Ohne Gentechnik” Add-on enables aquaculture, compound feed, and supply chain stakeholders to demonstrate that their products are free from GMOs.
Integrated Farm Assurance for aquaculture
IFA is a global standard that aims to promote safer and more responsible farming practices in aquaculture production.
GLOBALG.A.P. Chain of Custody
CoC is a supply chain standard that safeguards the segregation and traceability of products originating from GLOBALG.A.P. certified production processes.

Ready to get started?
Use our Smart Checklist Builder to easily understand which GLOBALG.A.P. smart farm assurance solutions are recommended for your production practices and generate a personalized checklist for your self-assessment.
Your guide to implementation
How to prepare for a Compound Feed Manufacturing audit
Learn more about the key documents and fee structure of Compound Feed Manufacturing (CFM). Follow our five steps to certification for an overview of the certification process, and find a GLOBALG.A.P. approved certification body (CB) in your area to get started.
Implementation and CB audit process
How does the CB audit process work?
CFM compliance is audited annually by accredited and independent third-party CBs.
Manufacturers can choose from any GLOBALG.A.P. approved CB active in the relevant country.
A successful CB audit results in a certificate valid for one year.
The CB is responsible for uploading the audit report and maintaining the accuracy of data in the GLOBALG.A.P. IT platform.
Manufacturers will be audited annually by a CB as part of the renewal process.
Which documents are required?
GLOBALG.A.P. general regulations and CFM general rules: Rules that define how the certification process works, from the scope of the standard to the audit requirements.
Control points and compliance criteria (CPCCs): Control points are the fundamental requirements for each standard. They are written in question form and are accompanied by corresponding compliance criteria that detail the various ways in which a producer can demonstrate compliance.
Checklist: The full list of CPCCs as used by CB auditors, enabling manufacturers to conduct a self-assessment in preparation for the CB audit.
Which versions of CFM are currently valid?
There is currently one valid version of CFM:
CFM v3.1 was published on 20 December 2022. It replaced v2.2 and v3 on 1 January 2024.
The FAQ contains further information on documents, certification renewal, and more.

What are the CFM standard requirements?
CPCCs are graded in three levels: Major Must, Minor Must, and Recommendation.
To achieve certification, manufacturers must comply with 100% of the Major Musts and at least 95% of the Minor Musts.
Corrective actions must be proposed for all non-compliances and submitted to the CB within the specified period.
Non-compliances must then be verified as corrected and compliant by the CB before a certificate can be issued.
Section C of CFM v3.1 contains 33 optional CPCCs. The section “Additional environmental and social governance” can be customized by a manufacturer in whole or by subsection and is indicated on the CFM certificate as a “specific product attribute.”
How much does CFM certification cost?
Each manufacturing operation is unique, and the total costs of certification depend on a combination of factors such as mill size, number of sites, location, necessary preparation measures (such as establishing new procedures), and more. CFM contains three cost elements:
Implementation costs: Incurred by the manufacturer to prepare for the CB audit
CB service fees: Determined and invoiced by the CB to cover audit time and travel costs
GLOBALG.A.P. registration and certificate license fees: Calculated based on quantity (metric tons) of feed produced annually and invoiced by the CB
For CFM, the minimum audit duration for the first manufacturing site is two days, and the minimum duration for each additional site is 0.75 days. This includes the audit and audit reporting, but excludes CB travel time.
The GLOBALG.A.P. fee table contains full information on the fee structure for each standard and add-on.
Five steps to certification

You will need the GLOBALG.A.P. general regulations, the CFM general rules, the CFM CPCCs, and the checklist. All of the required documents are available online, for free, and in multiple languages. They are linked below and can also be found in the GLOBALG.A.P. document center.

Use the documents to guide the implementation of the standard requirements, and then
conduct a self-assessment using the checklist. Our worldwide network of Registered Trainers
can also provide assistance during audit preparations.

Search the list of GLOBALG.A.P. approved CBs by region, country, scope, and status. Contact the CB of your choice and request an audit. Note that the GLOBALG.A.P. fee table does not cover CB service fees such as audit time or travel costs to your site.

The CB will conduct the audit and upload the results to the GLOBALG.A.P. IT platform. Any non-compliances which are detected during the CB audit must be corrected within the specified period and verified by the CB before a certificate can be issued.

Once all requirements are met and verified by the CB, they will issue your CFM certificate. Your certification status is then publicly visible in the GLOBALG.A.P. IT platform for transparency in the market.
Key documents
The three most relevant documents are linked below. Click ‘view more’ to see further related documents. Remember to always check with your CB that you have all necessary documents prior to audit.
CFM
Checklists
V3.1
English | Last updated: 29/11/2024
xlsx
Checklists
V3.1
English | Last updated: 29/11/2024
xlsx
Checklists are documents containing standard/add-on principles and criteria which are used during the audit/assessment to check whether compliance is achieved. They may also be used to conduct self-assessments.
CFM
Principles and criteria (P&Cs) (CPCCs)
V3.1
English | Last updated: 29/11/2024
Principles and criteria (P&Cs) (CPCCs)
V3.1
English | Last updated: 29/11/2024
Principles and criteria are a complete list of the requirements for a given standard or add-on. The foundational requirements each detail an outcome that must be achieved, and the corresponding ways in which compliance can be demonstrated.
CFM General Rules
Rules and regulations
V3.1
English | Last updated: 29/11/2024
Rules and regulations
V3.1
English | Last updated: 29/11/2024
Rules and regulations define how a specific standard must be implemented – from the certification scope to the audit requirements for certification bodies.
GLOBALG.A.P. approved CBs
The list of GLOBALG.A.P. approved CBs can be filtered by region, country, scope, and status. Click a CB to find more information and contact details.
If you do not filter your search, or filter only according to region and/or country, your search results will also show CBs that offer certification against benchmarked schemes, but which may not have approval for any GLOBALG.A.P. standards and add-ons.

Capacity building
Need assistance with the certification process? Our capacity-building program offers a range of options for training, consultation, and more!
A brief history of CFM
Development of CFM v1 begins in 2005. CFM v2 is launched in 2010, becoming the first global solution to cover both aquaculture and livestock compound feed under one standard.
GLOBALG.A.P. joins a selected group of experts from the aquaculture sector, academia, and NGOs to work with the International Sustainability Unit founded by HRH The Prince of Wales. Discussions on more sustainable and resilient fisheries lead to the launch of the ISU’s Marine Program and provide valuable input for the CFM revision.
CFM v2.1 is published in November 2011, and CFM certification then becomes obligatory for manufacturers that supply producers with IFA-certified production processes. The update includes new requirements on the responsible use of natural resources and the sourcing of fish meal/oil originating from wild marine species listed on the IUCN Red List. The first ten manufacturers achieve certification to CFM by the end of 2012. Two years later, this number rises to 96 manufacturers in 22 countries.
By 2018, there are 154 manufacturers under CFM certification in 32 countries. CFM-certified compound feed production processes account for 6.1 million metric tons of aquaculture feed and 8.8 million metric tons of livestock feed.
From February 2020, the CFM Focus Group, alongside stakeholders such as feed mill operators, ingredient suppliers, and producers, are consulted as part of the revision process for CFM v3. With new legislative requirements and growing consumer consciousness around the origins and sourcing of raw materials used to manufacture compound feed, there is major demand for the integration of stronger responsible raw material sourcing criteria.
CFM v3 is published in December 2021 and includes additional requirements on environmental protection, social responsibility, and economic viability. 170 manufacturers are now certified to CFM, producing over 23 million metric tons of aquaculture/livestock feed for the global market.
In 2022, the CFM Focus Group is asked to provide input on minor changes in the CFM general rules and CPCCs relating to their practical implementation. CFM v3.1 is published in December 2022. It replaces v2.2 and v3 on 1 January 2024.
FAQ
CFM v3.1 was published on 20 December 2022. It replaced v2.2 and v3 on 1 January 2024.
Each manufacturing operation is unique, and the total cost of certification depends on a combination of factors such as mill size, number of sites, location, existing policies and processes, etc. The invoice from your certification body (CB) will include CB service fees to cover expenditures (determined by the CB) and the GLOBALG.A.P. registration and certificate license fee.
Download the GLOBALG.A.P. fee table to learn more.
Section C of CFM v3.1 contains 33 optional CPCCs . The section, “Additional environmental and social governance,” can be customized by a manufacturer in whole or by subsection and is indicated on the CFM certificate as a “specific product attribute.” The CPCCs cover:
C) Additional environmental and social governance
C1 Environmental permits
C2 Fair operating practices
C3 Manufacturing process
C4 Labor practices
C5 Local community engagement
Manufacturers that seek to sell their feed to aquaculture producers with IFA-certified production processes must be certified to either CFM, a standard successfully benchmarked against CFM, or a feed scheme accredited to ISO/IEC 17065 or 17021.
The following third-party schemes are accepted as compliant with the sourcing requirements in Integrated Farm Assurance (IFA) for aquaculture:
FSSC Feed (including PAS 222)
SQF Code for Feed
Universal Feed Assurance Scheme (UFAS)
CFM documents are currently available in:
English
Spanish
All documents are located in the GLOBALG.A.P. document center. More languages are added based on demand – please contact us with requests.
CFM compliance is audited annually. The certification body (CB) audit must take place within the validity period of the current certificate in order for you to retain your certification status. Contact your CB to request an audit.
When developing our standards and add-ons, we aim to receive as much input and feedback as possible. With producers based in more than 135 countries around the world and stakeholders covering every part of the value chain, our standard-setting process ensures that our solutions are both fit for purpose now and built with the future in mind.
We offer public consultation periods for draft standard documents that are created by our technical experts. This helps to uphold transparency in the development, revision, and decision-making processes. The web page on standard setting outlines the development process.
Technical questions can be addressed to standard_support@agraya.com. Your query will be forwarded to the relevant technical expert.
The GLOBALG.A.P. Academy offers public trainings on our portfolio of smart farm assurance solutions, while our worldwide network of Registered Trainers offers authorized trainings and other services. See the GLOBALG.A.P. Academy course catalog or find a Registered Trainer for more information.
The CB auditor requirements for CFM are detailed in sections 6 of “GLOBALG.A.P. Compound Feed Manufacturing general rules”.
Learn more about how to become a GLOBALG.A.P. approved CB or extend your auditing scope.
No, certification to a GLOBALG.A.P. standard/holding a GLOBALG.A.P. certificate is not the same as being a GLOBALG.A.P. Community Member.
GLOBALG.A.P. Community Membership is a paid partnership opportunity, offering a variety of benefits including the ability to support the development of GLOBALG.A.P. standards and add-ons, contribute to the GLOBALG.A.P. governance structure, and access discounted services.
Learn more about how to become a GLOBALG.A.P. Community Member.
GLOBALG.A.P. trademarks may be used in a strictly B2B context and must be accompanied by a GLOBALG.A.P. identification number (e.g., the manufacturer’s GLOBALG.A.P. Number (GGN)) or a QR code to a manufacturer’s certification status in the GLOBALG.A.P. IT platform.
The GLOBALG.A.P. logo may be used on raw material products which are not for human consumption, and which are used as inputs for the production of the final products as listed in the GLOBALG.A.P. product list – for example, compound feed from CFM-certified production processes. Products sold to entities which do not use the products themselves (e.g., traders) and do not have GLOBALG.A.P. Chain of Custody certification cannot feature and/or be labeled with GLOBALG.A.P. trademarks, identification numbers, or a GLOBALG.A.P. claim.
Download the GLOBALG.A.P. trademarks use: policy and guidelines and GLOBALG.A.P. trademarks use: FAQ documents for comprehensive information on rules and use cases.

Contact us
For technical/interpretation questions, please contact us at standard_support@agraya.com.
For questions about the audit process or the GLOBALG.A.P. IT platform, please contact us at customer_support@globalgap.org.