Core solution
GLOBALG.A.P. Chain of Custody
The GLOBALG.A.P. Chain of Custody (CoC) standard ensures that any product sold with a GLOBALG.A.P. claim or bearing a GGN label logo is truly sourced from a GLOBALG.A.P. certified production process.
Facilitating transparency from farm to retailer
What is GLOBALG.A.P. Chain of Custody?
GLOBALG.A.P. Chain of Custody (CoC) allows supply chain stakeholders to demonstrate management systems that protect the segregation, identification, and traceability of products originating from GLOBALG.A.P. certified production processes. This way, products produced in line with safe, socially and environmentally responsible farming practices can be connected with a GLOBALG.A.P. claim at the end of the chain – reducing integrity risks, providing reassurance to customers, and adding value to a brand in the market. Applicable to products originating from production processes certified to Integrated Farm Assurance (IFA) or Compound Feed Manufacturing (CFM), CoC is tried, tested, and trusted around the world, with certificate holders operating in over 50 countries.
CoC at a glance
Applies to a wide range
of types and sizes of supply chain companies – from packers and processors to retailers and restaurants
Relevant for supply chain
companies sourcing from IFA- or CFM-certified production processes
Connects certified
responsible farming practices with a transparent GLOBALG.A.P. claim at the end of a custodial sequence
Establishes consistent
certification requirements and monitoring tools, mitigating the risk of food fraud or traceability issues
Reduces risk
of substitution, dilution, and misidentification of products originating from GLOBALG.A.P. certified production processes
Contributes to
accelerating global food sector transformation towards the UN Sustainable Development Goals
What is a GLOBALG.A.P. claim?
A GLOBALG.A.P. claim occurs when a GLOBALG.A.P. certificate holder, or a holder of a certificate for a benchmarked scheme or checklist, states and/or markets in a B2B context that a process, service, or product complies with a GLOBALG.A.P. standard or add-on. This includes on-product labeling with a GLOBALG.A.P. identification number.
The visual elements of the consumer-facing GGN label refer to the GGN label logo, the GLOBALG.A.P. Number (GGN) and/or CoC Number of the GGN label license holder, and the GGN label claim when applied to any product (packaging).
Which topics does CoC address?
International supply chains contain multiple stages. This means that not all supply chain companies source directly from producers with GLOBALG.A.P. certification. CoC is designed to identify products originating from GLOBALG.A.P. certified production processes and safeguard this status at every stage of the supply chain.
CoC is built on five key principles:
Supply chain companies must purchase products with a GLOBALG.A.P. claim from certified suppliers.
Products originating from GLOBALG.A.P. certified production processes must be separated from products originating from noncertified production processes at all times.
Products originating from GLOBALG.A.P. certified production processes must be clearly identified.
Products originating from GLOBALG.A.P. certified production processes must be traceable.
The company management system must ensure compliance with the CoC requirements.
Continuously improved through collaboration with the technical committees and worldwide network of GLOBALG.A.P. Community Members, our approach to standard setting ensures that CoC remains robust, realistic, and cost-efficient while meeting evolving market demands.
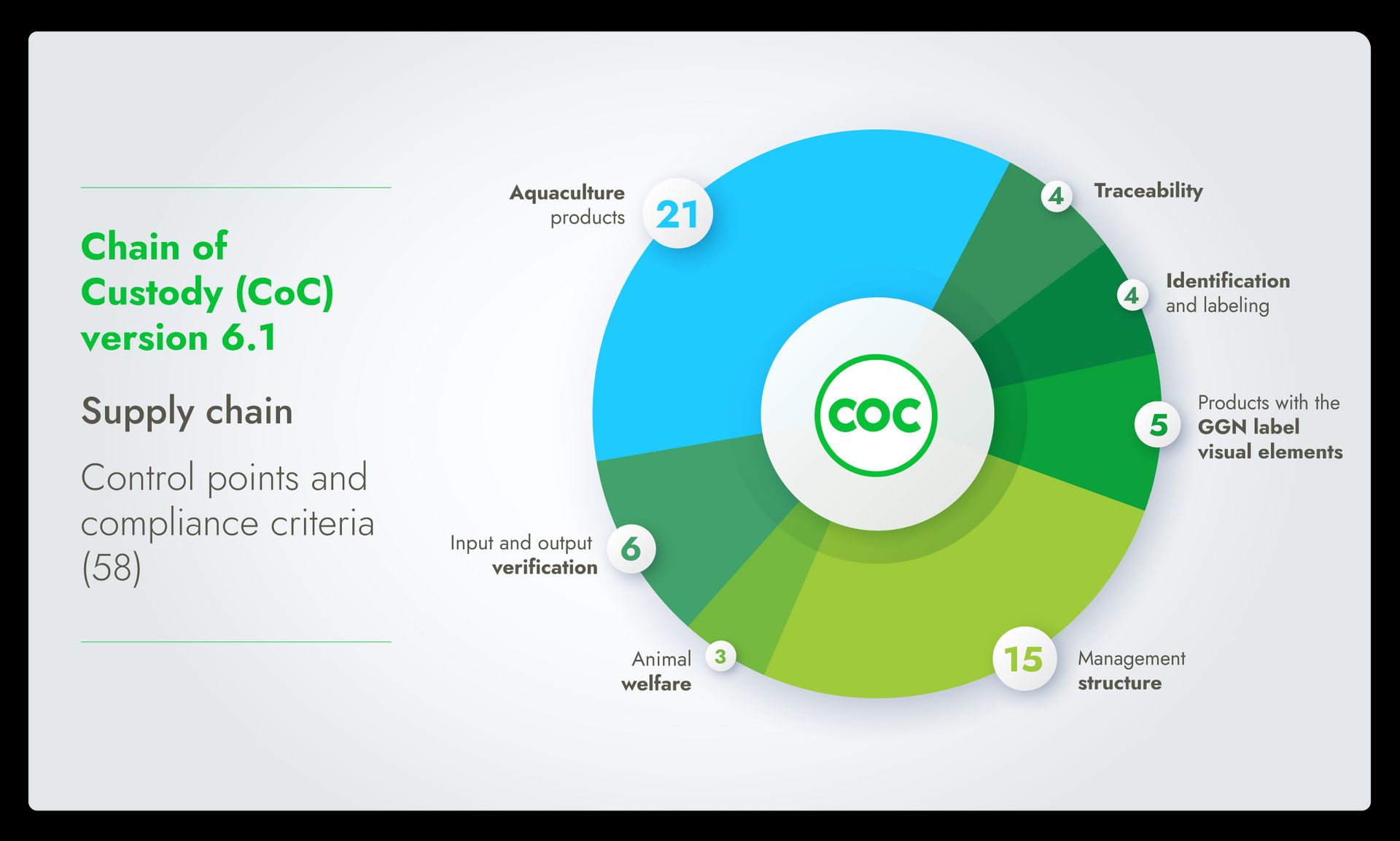
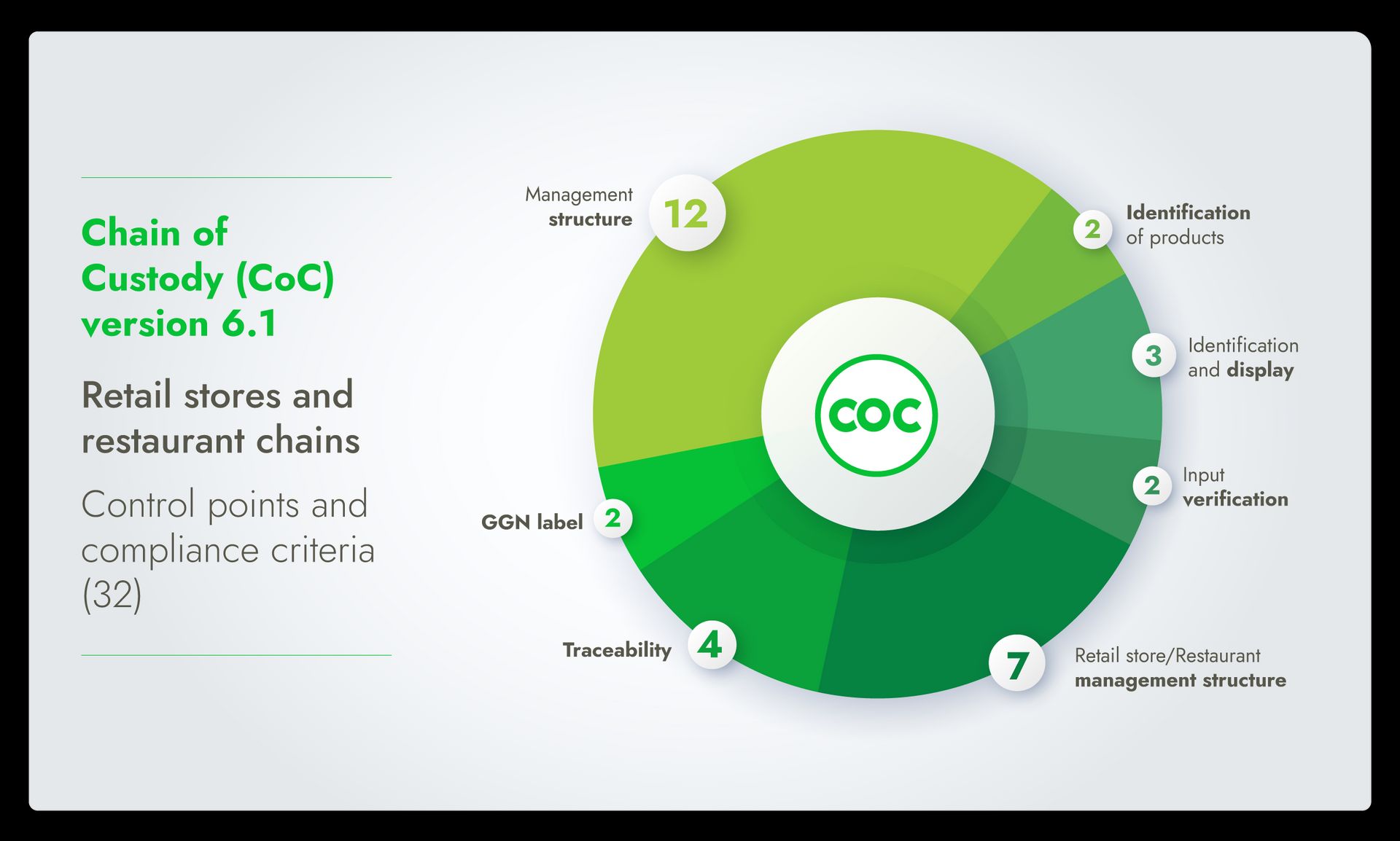
Core topics in CoC v6.1 include:
Management structure
Retail store/Restaurant management structure
Input and output verification
Traceability
Identification and labeling
Identification and display
Products with the GGN label visual elements
Aquaculture products
Animal welfare
Food safety and exceedances
Discover more about how CoC helps you address supply chain challenges.
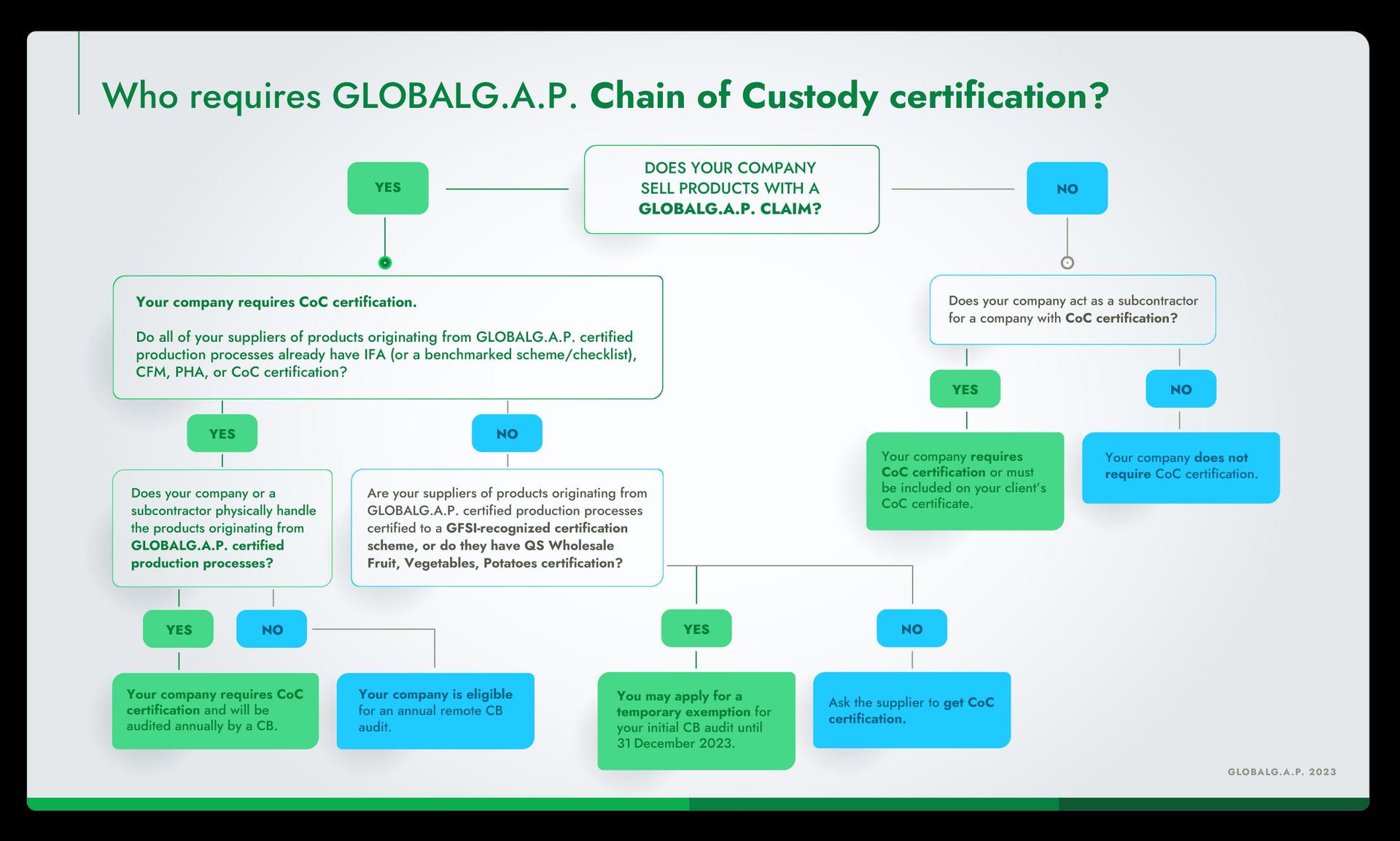
Who should use CoC?
CoC is an essential tool for any company handling or trading in products originating from GLOBALG.A.P. certified production processes. The standard applies to a wide range of types and sizes of companies in the supply chain that sell products with a GLOBALG.A.P. claim, including subcontractors who handle the products:
Producers
Packers
Brokers
Processors
Logistics companies
Retailers
Restaurants
The standard covers all products under the IFA scopes of plants and aquaculture, as well as animal feed produced under the CFM standard.
CoC certification is available for companies (legal entities) under Option 1, meaning that if the company operates more than one site, all sites must be audited individually.
Stakeholders to which CoC certification does not apply
How does CoC work?
Compliance with the standard requirements is audited annually by an accredited and independent third-party certification body (CB).
Companies can choose from any GLOBALG.A.P. approved CB active in the relevant country
A successful CB audit results in a certificate valid for one year.
The standard is composed of control points and compliance criteria (CPCCs). CPCCs are graded in three levels: Major Must, Minor Must, and Recommendation.
Control points
Fundamentals that set the foundation of a GLOBALG.A.P. requirement
Written in question form
Compliance criteria
Methods that producers can use to demonstrate a control point to be true
Evidence required for demonstrating that the outcome is achieved
Read more about the audit process and standard requirements.
How is certification status verified?
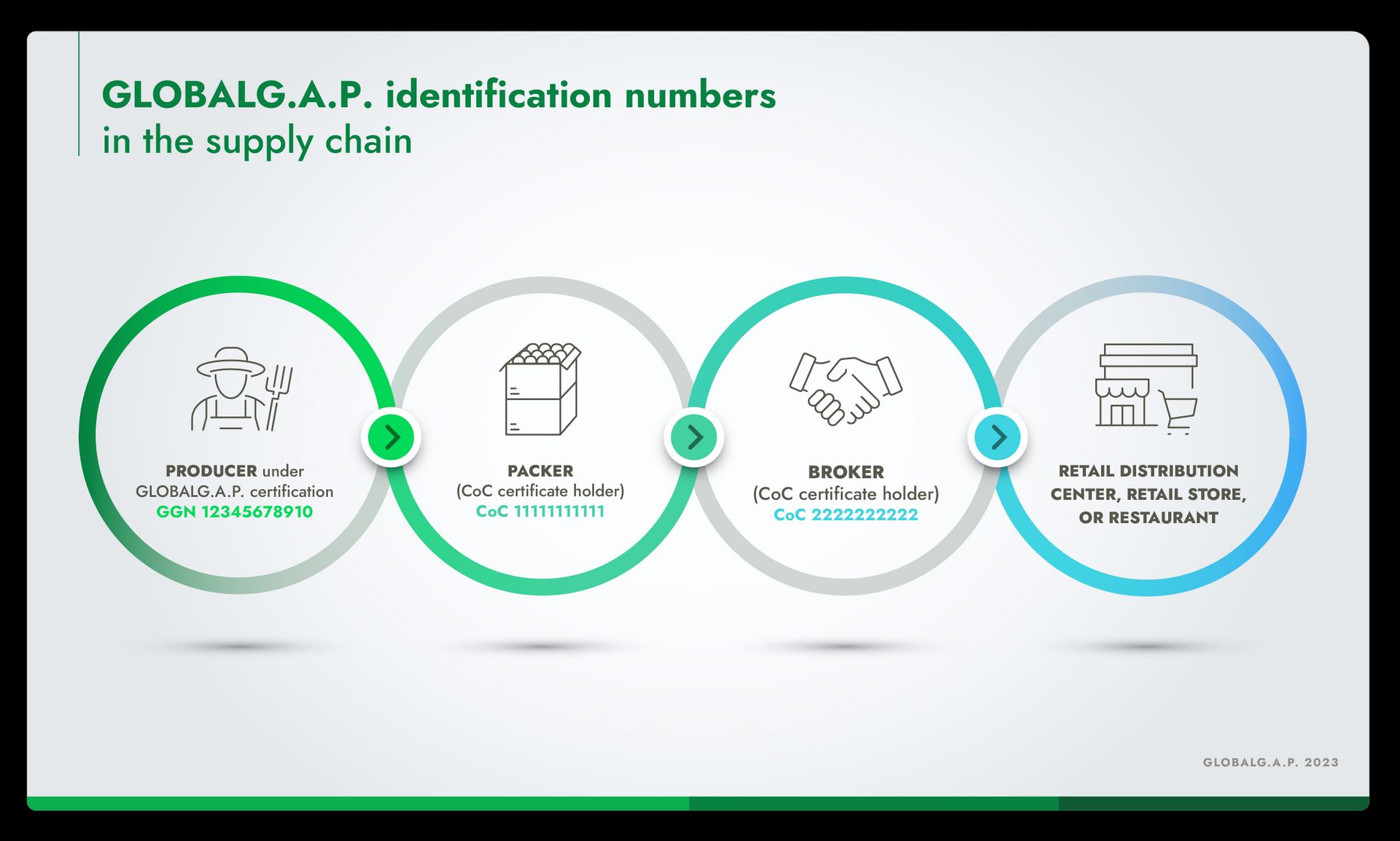
Every supply chain company registered in the GLOBALG.A.P. certification system is assigned a 13-digit GLOBALG.A.P. identification number such as a GLOBALG.A.P. Number (GGN) or a CoC Number. A GGN is linked to a producer (any activity related to IFA or CFM), while a CoC Number is linked to a company with CoC certification (any activity related to the supply chain).
These numbers are linked to a legal entity – a producer or supply chain company – for as long as that entity exists. This allows real-time verification of certification status in the GLOBALG.A.P. IT systems, upholding our rigorous transparency requirements throughout the supply chain.
Supply chain stakeholders can control data access and privacy rights for audit reports, and the reports are not shared publicly or with third parties. This process is handled via your chosen CB.
Combined CoC audits
As part of our mission to reduce duplication in supply chains, we have worked in collaboration with other certification schemes to offer combined audits with the GLOBALG.A.P. CoC standard.
The following options are not GLOBALG.A.P. benchmarked schemes, but offer a combined audit approach designed to save resources by auditing only the parts of the CoC checklist that are not covered by the below standards:
CoC through BRCGS
BRCGS Food Safety standardsCoC through IFS
IFS Food Safety standardsCoC through QS
QS Wholesale Fruit, Vegetables, PotatoesCoC through AMA
AMA Quality Seal Guideline “Fruits, Vegetables, Potatoes”
Only GLOBALG.A.P. approved CBs may conduct the CoC combined audits, and a successful audit will result in two separate certificates. Certification status is then visible in the GLOBALG.A.P. IT systems for transparency in the market.
Latest news
11 April 2024
New GLOBALG.A.P. webinar series: A guide to IFA v6 transition
Hosted by GLOBALG.A.P. experts, our latest free webinar series is designed to help producers transition seamlessly to IFA version 6 for flowers and ornamentals, fruit and vegetables, and aquaculture. Find your webinar today!
26 March 2024
Exploring Fish International 2024
Read about our experience at Fish International 2024, the biennial German trade fair for the fish and seafood sector held in Bremen. As usual, the GLOBALG.A.P. and GGN label brands shared an exhibition booth and our experts enjoyed meeting you there.
Looking for technical news?
Technical news updates for core solutions can be found in our technical news libraries.
Making responsible farming visible to consumers
CoC certification is one of the requirements for using the GGN label – a consumer label for certified, responsible farming and transparency found on fruit and vegetables, farmed seafood, flowers, and plants. Improve your competitive edge and grow trust in your brand by making responsible farming visible on store shelves!
Safeguard supply chain integrity
Why choose GLOBALG.A.P. Chain of Custody?
GLOBALG.A.P. Chain of Custody (CoC) certification protects the integrity of products originating from GLOBALG.A.P. certified production processes. Requested by buyers across the globe, the standard outlines a practical path for supply chain companies to implement and demonstrate effective management systems for the handling and trading of these products. CoC therefore helps mitigate reputational risks and builds confidence in increasingly complex global value chains.
Which industry challenges does CoC address?
Implementing safer and more sustainable farming practices is a core demand of retailers and consumers around the world.
Achieving recognition for these practices through certification takes significant time, effort, and investment from producers at farm level.
However, the value of responsible farming practices is significantly reduced if they cannot be transparently linked to a GLOBALG.A.P. claim at the end of the supply chain.
If segregation and traceability are lacking, the reputational risk for buyers increases – through food fraud or the inability to trace a product if, for example, a food safety issue arises.
Supply chain companies therefore need consistent certification requirements and monitoring tools to ensure that the integrity of products is protected up to the final sale.
As global supply chains grow in complexity, CoC certification provides reassurance to customers and adds value to a brand in the market.
Follow our five steps to certification to get started today.
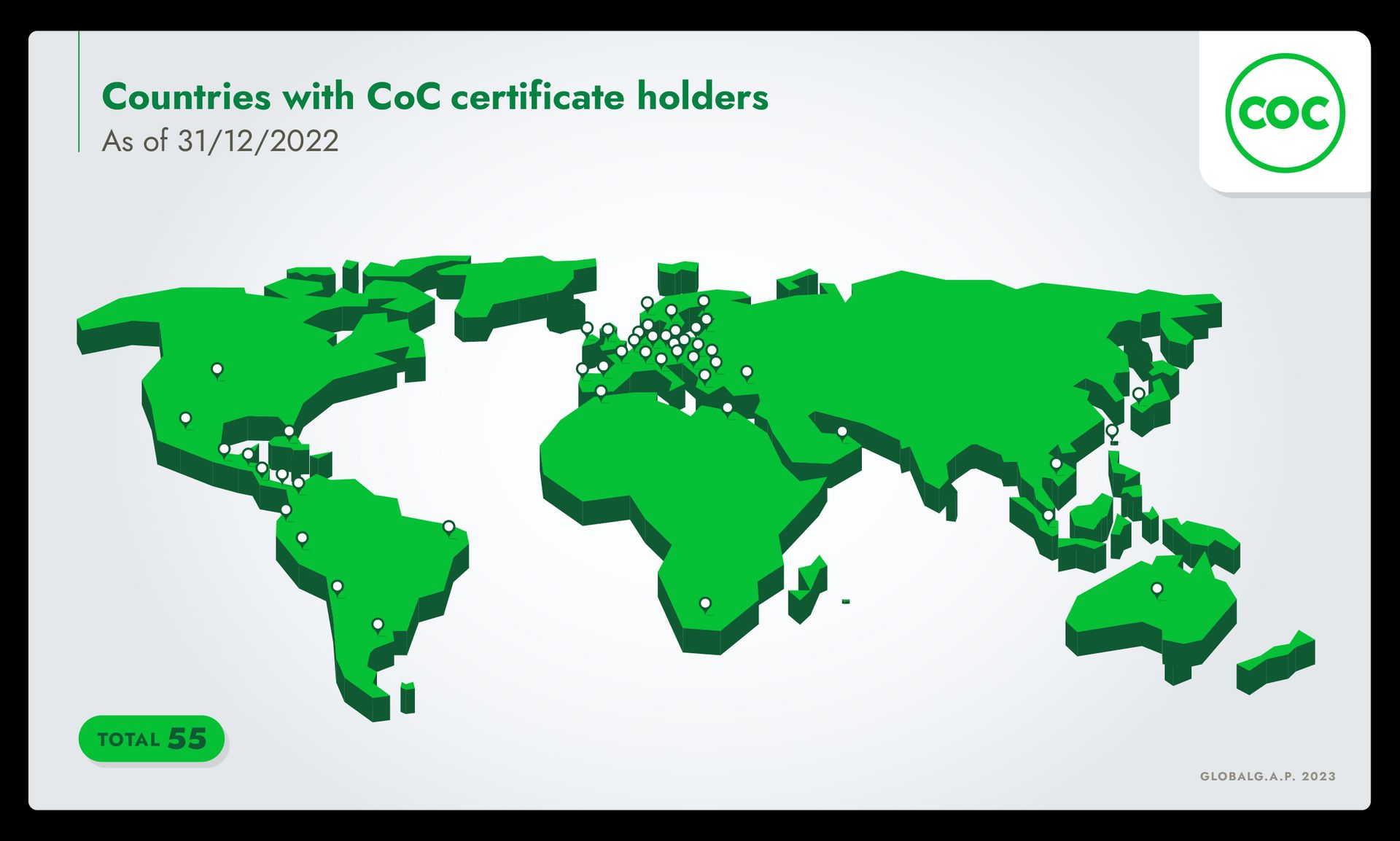
CoC in numbers (as of 31/12/2022)
3,342
companies under certification
55
countries with CoC certificate holders
132
Traders with CoC certification participating in the GGN label initiative
What are the benefits for supply chain companies?
Reduce the risk of substitution, dilution, and misidentification of products originating from GLOBALG.A.P. certified production processes
Improve segregation methods and traceability systems in the supply chain
Enable a quick response if issues arise through transparency and risk monitoring
Reflect the certified company’s commitment towards safer and more sustainable farming practices
Apply the standard to a wide range of types and sizes of supply chain companies globally
Add value to brands in the market and provide assurance to customers
A few years ago, we started our path with GLOBALG.A.P. CoC certification. It has certainly helped us to strengthen our policies and has opened doors for us to work with certain clients. Both the GLOBALG.A.P. Secretariat and our CB have been supporting us with any doubts that have arisen, making the certification process easy and agile.
Victor Abad Lopez
Quality and Food Safety Head Manager at Compesca | Spain
Maintaining trust in GLOBALG.A.P. certification
The GLOBALG.A.P. Integrity Program was founded in 2008 as the first of its kind in food certification. Designed to ensure the consistent delivery and implementation of GLOBALG.A.P. standards and add-ons worldwide, the program monitors and assesses all aspects of the third-party certification process.
Which solutions can be combined with CoC?
We offer a range of standards and add-ons targeted to specific aspects of production and the supply chain.
Learn more about GLOBALG.A.P. smart farm assurance solutions.
You may also be interested in...
Integrated Farm Assurance for fruit and vegetables
IFA is a global standard for safe and responsible farming practices in fruit and vegetable production.
Integrated Farm Assurance for flowers and ornamentals
IFA is a global standard for safe and responsible farming practices in flower and ornamental production.
Integrated Farm Assurance for aquaculture
IFA is a global standard for safe and responsible farming practices in aquaculture production.
Ready to get started?
Use our Smart Checklist Builder to easily understand which GLOBALG.A.P. smart farm assurance solutions are recommended for your production practices and generate a personalized checklist for your self-assessment.
Your guide to implementation
How to prepare for a GLOBALG.A.P. Chain of Custody audit
Learn more about the key documents and fee structure of GLOBALG.A.P. Chain of Custody (CoC). Follow our five steps to certification for an overview of the certification process, and find a GLOBALG.A.P. approved certification body (CB) in your area to get started.
Specific requirements for supply chain companies
Implementation and CB audit process
How does the CB audit process work?
CoC compliance is audited annually by accredited and independent third-party CBs.
Companies can choose from any GLOBALG.A.P. approved CB active in the relevant country.
A successful CB audit results in a certificate valid for one year.
The CB is responsible for uploading the audit report and maintaining the accuracy of company data in the GLOBALG.A.P. IT systems.
Companies will be audited annually by a CB as part of the renewal process.
Which documents are required?
GLOBALG.A.P. general regulations: Rules that define how the certification process works, from the scope of the standard to the audit requirements.
Control points and compliance criteria (CPCCs): Control points are the fundamental requirements for each standard. They are written in question form and are accompanied by corresponding compliance criteria that detail the various ways in which a company can demonstrate compliance.
Checklist: The full list of CPCCs as used by CB auditors, enabling companies to conduct a self-assessment in preparation for the CB audit.
Which version of CoC is currently valid?
CoC v6.1 is the only valid version currently available for certification. It was published in November 2022 and became obligatory on 1 July 2023.
The FAQ contains more information on documents, certification renewal, and more.
What are the CoC standard requirements?
CPCCs are graded in three levels: Major Must, Minor Must, and Recommendation.
To achieve certification, companies must comply with 100% of the Major Musts and at least one of the two Minor Musts.
Corrective actions must be proposed for all non-compliances and submitted to the CB within the specified period.
Non-compliances must then be verified as corrected and compliant by the CB before a certificate can be issued.
How much does CoC certification cost?
Each company is unique, and the total costs of certification depend on a combination of factors such as company size, number of sites, location, necessary preparation measures (such as establishing new procedures), and more. CoC contains three cost elements:
Implementation costs: Incurred by the company to prepare for the CB audit
CB service fees: Determined and invoiced by the CB to cover audit time and travel costs
GLOBALG.A.P. registration and certificate license fees: Annual fee invoiced by the CB for each registered and certified company
The GLOBALG.A.P. fee table contains full information on the fee structure for each standard and add-on.
Five steps to certification
You will need the CoC general regulations, the CoC CPCCs, and the checklist. All of the required documents are available online, for free, and in multiple languages. They are linked below and can also be found in the GLOBALG.A.P. document center.
Train staff and nominate your company’s CoC representative. Use the documents to guide the implementation of the standard requirements, and then conduct a self-assessment using the checklist. Our worldwide network of Registered Trainers can also provide assistance during audit preparations.
Search the list of GLOBALG.A.P. approved CBs by region, country, scope, and status. Contact the CB of your choice and request an audit. Note that the GLOBALG.A.P. fee table does not cover CB service fees such as audit time or travel costs to your site.
The CB will conduct the audit and upload the results to Audit Online Hub. Any non-compliances which are detected during the CB audit must be corrected within the specified period and verified by the CB before a certificate can be issued.
Once all requirements are met and verified by the CB, they will issue your CoC certificate. Your certification status is then publicly visible in the GLOBALG.A.P. IT systems for transparency in the market.
Key documents
The three most relevant documents are linked below. Click ‘view more’ to see further related documents. Remember to always check with your CB that you have all necessary documents prior to audit.
CoC
Checklists
V6.1
English | Last updated: 11/03/2024
xlsx
Checklists are documents containing standard/add-on principles and criteria which are used during the audit/assessment to check whether compliance is achieved. They may also be used to conduct self-assessments.
CoC
GLOBALG.A.P. general regulations
V6.1
English | Last updated: 11/03/2024
GLOBALG.A.P. general regulations outline the framework of the certification system, including the role and relationship of the GLOBALG.A.P. Secretariat and certification bodies, and provide context for implementing checklist content.
CoC
Principles and criteria (P&Cs) (CPCCs)
V6.1
English | Last updated: 11/03/2024
Principles and criteria are a complete list of the requirements for a given standard or add-on. The foundational requirements each detail an outcome that must be achieved, and the corresponding ways in which compliance can be demonstrated.
GLOBALG.A.P. approved CBs
The list of GLOBALG.A.P. approved CBs can be filtered by region, country, scope, and status. Click a CB to find more information and contact details.
If you do not filter your search, or filter only according to region and/or country, your search results will also show CBs that offer certification against benchmarked schemes, but which may not have approval for any GLOBALG.A.P. standards and add-ons.
Capacity building
Need assistance with the certification process? Our capacity-building program offers a range of options for training, consultation, and more!
Upcoming events
22 Apr - 26 Apr
2024
Academy training: IFA v6 for fruit and vegetables in French
Location:
Online
Event type:
Academy course
Event format:
Virtual
23 Apr - 25 Apr
2024
Seafood Expo Global 2024
Location:
Barcelona, Spain
Event type:
Trade fair
Event format:
On-site
A brief history of CoC
CoC development begins in 2004, and version 1 of the standard – applicable to aquaculture products only – is published in June 2005. The standard is revised and CoC v2 is launched in May 2008.
CoC v3 is released in January 2010, expanding the scope of products covered to include tea and coffee. CoC is made mandatory from the first postharvest processing step.
In 2013, CoC v4 is expanded to include fruit and vegetables, flowers and ornamentals, and more, in addition to aquaculture and livestock. In 2014, public consultation takes place for the revised CoC v5, which is launched in December.
By 2016, there are almost 500 CoC certificate holders. This number rises to 749 in 2017, handling more than five million metric tons of plants and two million metric tons of aquaculture products. By 2018, the number of CoC certificate holders passes 1,000, with certified companies in 38 countries. CoC v6 is published in September 2019, and by the end of the year, there are 1417 certificate holders across 45 countries worldwide.
The revision process for CoC v6 is initiated in 2021, and v6.1 is published in November 2022. By the end of 2022, there are 3342 CoC certificate holders in 55 countries. CoC v6.1 replaces v6 and becomes obligatory in July 2023.
FAQ
Contact us
For technical/interpretation questions, please contact us at standard_support@globalgap.org.
For questions about the audit process or GLOBALG.A.P. IT systems, please contact us at customer_support@globalgap.org.